The first Norwegian CAR
Made in Oslo by a team of researchers from Oslo University Hospital, the first ever Norwegian CAR T cell is now a fact. A potential treatment based on this result depends on a clinical study.
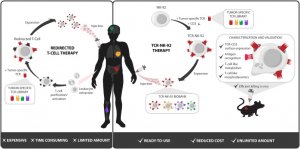
A new Norwegian study shows a genetically modified cell-line with great potential as treatment for patients that are not responding to established CAR T cell therapies. This form of immuno-therapy for cancer patients has recently been approved in many countries, including Norway.
“We hope that the Norwegian authorities will be interested in transforming this research into benefits for Norwegian patients.” Hakan Köksal
What is a CAR?
Before we go into the research, let us clarify an essential question. What is a CAR? Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells are T cells that have been genetically engineered to produce an artificialreceptorwhich binds a protein on cancer cells.
How does this work? T cells naturally recognize threats to the body using their T cell receptors, but cancer cells can lock onto those receptors and deactivate them. The new CAR T cell therapies are in fact genetic manipulations used to lure a T cell to make it kill cancer cells. This is what a CAR is doing, indeed CARs replace the natural T-cell receptors in any T cells and give them the power to recognize the defined target – the cancer cell.
CAR-T cell therapy is used as cancer therapy for patients with B-cell malignancies that do not respond to other treatments.
A severe consequence of using CAR T cell therapy is that it effectively wipes out all the B cells in the patient’s body — not only the cancerous leukemia cells or the lymphoma, but the healthy B cells as well. Since B-cells are an important part of the immune system, it goes without saying that the treatment comes with risks.
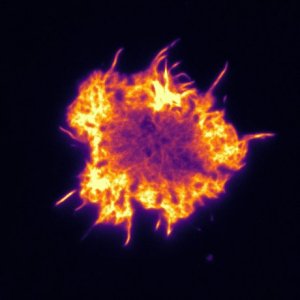
Micrograph of actin cytoskeleton of T-cells. The cell is about 10µm in diameter. Photo: Pierre Dillard
Made in Norway
Now let us move on to the new research. This particular construct was designed from an antibody that was isolated in the 1980’s at the Radium Hospital in Oslo.
The CAR construct was designed, manufactured and validated in two laboratories in the Radium Hospital campus. One is the laboratory of Immunomonitoring and Translational Research of the Department of Cellular Therapy, OUH, located at the Oslo Cancer Cluster Incubator. This laboratory is led by Else Marit Inderberg and Sébastien Wälchli. The other is the laboratory of the Lymphoma biology group of the Department of Cancer Immunology, Institute for Cancer Research, OUH. This laboratory is led by June Helen Myklebust and Erlend B. Smeland.
“Even the mouse was Norwegian.” Hakan Köksal
The pre-clinical work that made the Norwegian CAR was completed in March 2019.
In the research paper “Preclinical development of CD37CAR T-cell therapy for treatment of B-cell lymphoma”, published in the journal Blood Advances, the research team tests an artificially produced construct calledCD37CAR and finds that it is especially promising for patients suffering from multiple types of B-cell lymphoma. This may be treated successfully with novel cell-based therapy.
It now needs to be approved by the authorities and gain financial support to be further tested in a clinical study in order to benefit Norwegian patients.
The first CAR-therapy
CAR-based therapy gained full attention when the common B-cell marker CD19 was targeted and made the basis for the CAR T cell therapy known as Kymriah (tisagenlecleucel) from Novartis.
It quickly became known as the first gene therapy allowed in the US when it was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) just last year, in 2018, to treat certain children and young adults with B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Shortly after, the European Commission also approved this CAR T cell therapy for young European patients. The Norwegian Medicines Agency soon followed and approved the treatment in Norway.
“CD19CAR was the first CAR construct ever developed, but nowadays more and more limitations to this treatment have emerged. The development of new CAR strategies targeting different antigens has become a growing need.” Dr. Pierre Dillard
Not effective for all
Although the CD19CAR T cell therapy has shown impressive clinical responses in B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, not all patients respond to this CAR T treatment.
In fact, patients can become resistant to CD19CAR. Such relapse has been observed in roughly 30% of the studies of this treatment. Thus, alternative B-cell targets need to be discovered and evaluated. CD37 is one of them.
“You could target any antigen to get a new CAR, but it is always a matter of safety and specificity.” Hakan Köksal said.

Dr. Pierre Dillard and Hakan Köksal are part of the team behind the new study on CD37CAR T-cell therapy for treatment of B-cell lymphoma.
The Norwegian plan B
The novel Norwegian CAR T is the perfect option B to the CD19CAR.
“The more ammunition we have against the tumours, the more likely we are to get better response rates in the patients.” Hakan Köksal
The CD37CAR T cells tested in mouse models in this Norwegian study, show great potential as treatment for patients that are not responding to the established CD19CAR-treatment.
“More and more labs are studying the possibility of using CAR therapy as combination, i.e. CAR treatments targeting different antigens. Such a strategy will significantly lower the probability of patients relapsing.” Dr. Pierre Dillard said.
The CD37CAR still needs to be tested clinically. The scientists at OUS underline the importance of keeping the developed CD37CAR in Norway and having it tested in a clinical trial.
“It is a point to keep it here and potentially save patients here. We would like to see the first CD37CAR clinical study here in Norway.” Hakan Köksal
More from the Translational Research Lab of the Department of Cellular Therapy, OUH:
- New research: 3D structure tumors in immunotherapy
- Natural killer cells dressed to kill cancer cells
- How Cancer Research Becomes a Company